Define Polarizability and Explain How It Is Different From Polarity
The polarizability - Polar molecules - Nonpolar molecules - Induced dipoles - Ferroelectric materials. 210 α m E.
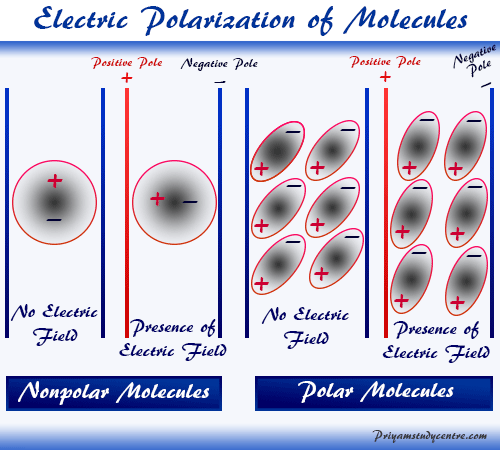
Electric Polarization Definition Types Formula Units
A dielectric may be made up of polar or non-polar molecules.

. A non-polar molecule on the other hand is one which has no net dipole moment mostly due to equal sharing of electrons among the chemical species and a. Typically the electron cloud will belong to an atom or molecule or ion. The polarity of a molecule tells whether the electron cloud is equally distributed across the atoms within the molecule or whether an electronegative atom is affecting the electron density.
It is the multiple of such charge separated and distance between them. An important microscopic electrical parameter for dielectrics is polarizability or coefficient of polarization α. The main difference between the polar and the non-polar molecules is the temperature dependence of dipole moment in case of polar molecules and no such dependence in case of non-polar molecules.
If molecules can be polarized by the application of light or an electric field and if they are somewhat organized in a bulk material then the index of refraction of the substance can be altered allowing the switching or modulating of light passing through. Any bond between atoms of two different atoms is polar. A molecule is basically said to be either a polar molecule non- polar molecule or ionic molecule.
Polarizability is the relative tendency of a charge distribution in other words the more changes in the electron cloud geometry the greater the polarizability. The temperature dependence of these types of polarizability is slight. Polarazibility also affects dispersion forces through the molecular shape of the affected molecules.
This force is sometimes called an induced dipole-induced dipole attraction. Polarizability expresses the ability of atoms molecules or groups of a dielectric material to be polarized. When a molecule is said to have.
Define electronegativity and explain how it provides a measure for the polarity of a chemical bond. Polarization also polarisation is a property applying to transverse waves that specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. For linear dielectrics polarizability is defined as follows.
But the net effect of an external field is almost the same ie. POLARIZABILITY Having now revised the basics of trends across and down the Periodic Table we can use. That is bond polarity.
Polarization is an critical process in designing electro-optical materials. The electric field could be caused for example by an electrode or a nearby cation or anion. Explain how size affects polarizability.
Non-polar covalent polar covalent ionic Fajans rules for predicting whether a bond is. As the electronegativity of two atoms is different hence the bond will show dipolar nature positive and negative charge accumulation at opposite ends. Nonpolar molecules are of two types.
How is it possible for the molecule BeF to have polar covalent bonds yet be a nonpolar molecule or have a dipole moment of zero. Given the following compounds which one has a higher dipole moment. The polarizing power of a cation is proportional to its charge radius ratio.
Polarizability is a measure of how easily an electron cloud is distorted by an electric field. As the temperature rises the polarizability decreases somewhat. A polar molecule is usually formed when the one end of the molecule is said to possess more number of positive charges and whereas the opposite end of the molecule has negative charges creating an electrical pole.
Polarizability is the ease with which an electron distribution can be deformed making a molecule polar for a few moments in LD forces. Module 31 Objectives Define dispersion forces Explain occurrence Define dipole-dipole forces What types of molecules experience this type of IMF Define hydrogen-bonding Identify when they occur Identify relative energy range for IMFs compared to covalent bonds Determine IMFs for molecules based on structure Predict relative strengths for IMFs for a set of molecules Use. Solution for Define the following.
To explain how the dielectric constant relates to the electronic polarizability of a material the polarization or P of a material should be determined. In the physics of solid and liquid. Define electronegativity and use this concept to explain bond polarity.
This is illustrated in where a large and soft anion comes under the influence of a small cation. The larger the molecule the greater the of electrons the more polarizable it is. A polar molecule results when a molecule contains polar bonds in an unsymmetrical arrangement.
The power of an ion to destroy the other ion is known as its polar-izing power and the tendency of the ion to the ion to distort is known as its polarizability. Thus molecules attract one another more strongly and melting and boiling points of covalent substances increase with larger molecular mass. Define electronegativity and use this concept to explain the transition between pure covalent polar covalent and ionic bonds.
The London dispersion force is the weakest intermolecular force. To find the answer draw first its Lewis structure with correct geometry. For example you can predict which solvents will be most effective with a given chemical if you know its.
Define polarizability and how it affects LD forces. So a polar molecule is one which has a net dipole moment because of unequal sharing of electrons. The London dispersion force is a temporary attractive force that results when the electrons in two adjacent atoms occupy positions that make the atoms form temporary dipoles.
The distribution of the electrons will affect the behavior and reactivity of the molecule. As polarizability increases the dispersion forces also become stronger. If the anions were different then the answer could be affected by the variation of the anion Here the significant difference between the cations.
Atomic polarizability is due to the displacement in a field E of atoms of different types in a molecule and is related to the asymmetric distribution of electron density. A simple example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string see image. Dipole moment is the measure of that polarity.
For example in a musical instrument like a guitar string. The electronic polarizability is a microscopic polarization phenomena that occurs in all materials and is one of the main mechanisms that drives dielectric polarization. Molecules whose atoms have equal or nearly equal electronegativities have zero or very small dipole moments.
What Is Polarizability Of Anions Quora

No comments for "Define Polarizability and Explain How It Is Different From Polarity"
Post a Comment