Two Statistics Is Used to Describe a Normal Distribution
There are two main parameters of normal distribution in statistics namely mean and standard deviation. Range Standard Error of the Mean.
Normal Distribution Statistics The Ultimate Guide
A perfectly Normal distribution has Kurtosis 3 based on the above equation.

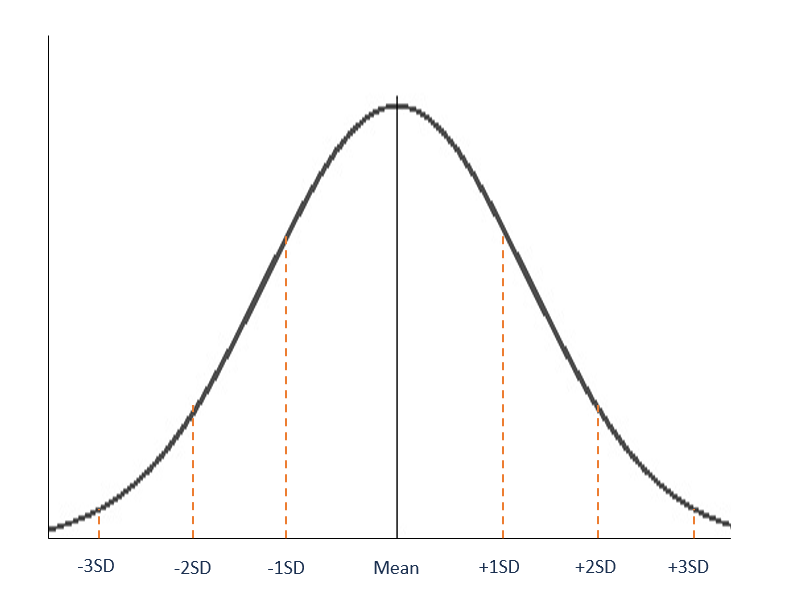
. We know that the two halves of the normal distribution are mirror images of each other. The shape of the distribution changes as the parameter values change. 2 If a normal distribution has a mean of 30 and a standard deviation of 5 then.
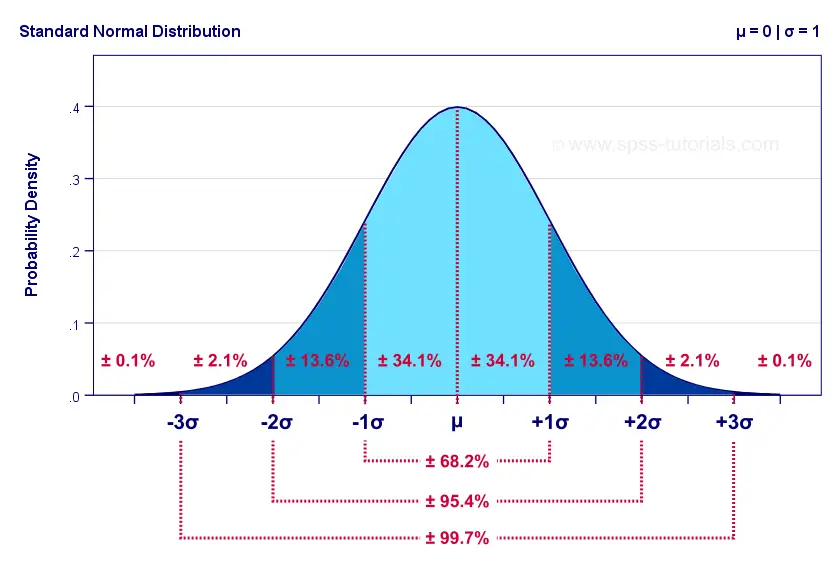
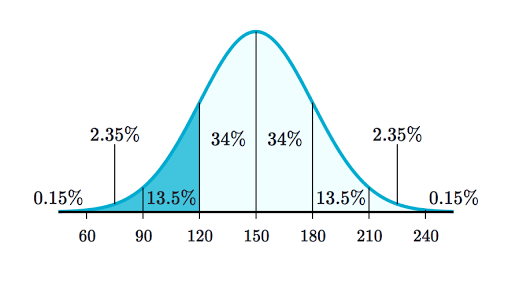
However SPSS and other statistical software packages subtract 3 from kurtosis values. Around 997 of values are within 3 standard deviations from the mean. Statistics - The Normal Distribution.
In a normal distribution the mean is zero and the standard deviation is 1. So if the area for the interval from -065 and 065 is 4843 then the range from 0 to 065 must be half of that. The total area under a normal distribution curve is equal to this.
Some of the important properties of the normal distribution are listed below. Measure of location of the centre of the curve. Kurtosis is a measure of the peakedness of a distribution.
The two main parameters of a normal distribution are the mean and standard deviation. X 5 212 74. Start studying CH3 Descriptive Statistics the Normal Distribution.
We will start with the standard normal distribution which is the simplest and then move to the more general form. What are the mean and standard deviation of the Z- distribution. Coefficient of Kurtosis Where.
Consider the supply chain for a plant that assembles industrial pumps. A normal distribution is a bell shaped curve. Symmetrical distributions are ones where the right and left halves are perfect mirrors of each other.
It occurs naturally in several cases. The central tendency concerns the averages of the values. X mean X i X value from individual i N sample size s standard deviation.
When P 005 null hypothesis accepted and data are called as normally distributed. Points on a test. The first distribution is unimodal it has one mode roughly at 10 around which the observations are concentrated.
Symmetrical distributions that are bell-shaped are also known as normal distributions An example of a normal distribution is pictured below. C bell curve Explanation. Distributions may also have a single peak or more than one peak.
For example the normal distribution can be seen in tests such as GRE and SAT. Additionally we know that the area for all scores less than zero is half 50 of the distribution. As scientists researchers and managers working in the natural resources sector we all rely on statistical analysis to help us answer the questions that arise in the.
The letter Z is often used to denote a random variable that follows this standard normal distribution. The standard normal distribution is a normal distribution with mean μ 0 and standard deviation σ 1. Around 95 of values are within 2 standard deviations from the mean.
The original kurtosis value is sometimes called kurtosis proper. A normal distribution is the proper term for a probability bell curve. Many organizations obtain their inputs though a supply chain.
For the standard normal distribution we define a random variable Z that has a mean of zero. The empirical rule or the 68-95-997 rule tells you where most of your values lie in a normal distribution. Because of this it is widely used in statistics business and government bodies like the FDA.
Probability of Simple Events 2. The second distribution is bimodal it has two modes roughly at 10 and 20 around which the observations are concentrated. 1 Which choice is another term that can be used to describe a normal distribution.
The variance and standard deviation are both 1. Standard Error of the Mean Standard Deviation. Types of descriptive statistics.
Although most statistics courses use unimodal distributions like the normal distribution to explain different topics bimodal distributions actually show up fairly often in practice so its useful to know how to recognize and interpret them. Which of the following two statistics is used to describe a normal distribution. OTHER SETS BY THIS CREATOR.
There are 3 main types of descriptive statistics. The mean is used by researchers as a measure of central tendency. If x is two standard deviations above its mean x equals the mean 5 plus 2 times the standard deviation 12.
There are two common ways of describing the normal distribution. Bi two uni one. Venn diagrams and Mutually Exclusive Events 2.
The variability or dispersion concerns how spread out the values are. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. One way to compute probabilities for a normal distribution is to use tables that give probabilities for the standard one since it would be impossible to keep.
Skewness is a measure of symmetry or more precisely the lack of symmetry of the normal distribution. Descriptive Statistics and the Normal Distribution. The location and scale parameters of the given normal distribution can be estimated using these two parameters.
Therefore a kurtosis value of 0 from SPSS indicates a perfectly Normal distribution. B the median is 30 and the mode is 30. The third distribution is kind of flat or uniform.
The Z- distribution also called the standard normal distribution has a. Statistics has become the universal language of the sciences and data analysis can lead to powerful results. The Central Limit Theorem say that given any probability distribution with a finite mean mu and standard deviation sigma then the sum of n samples will be approximately normally distribution with mean nmu and standard deviation sqrtnsigma while the average of n samples is approximately distributed with mean mu and standard distribution.
Furthermore there are several groups that follow the normal distribution pattern. A data set that has a normal distribution can be described by two numbers. A common term used to describe a normal distribution curve.
Around 68 of values are within 1 standard deviation from the mean. You can remember the difference between the two by remembering. For a normal distribution Mean Median Mode.
The parameters determine the shape and probabilities of the distribution. The distribution concerns the frequency of each value. The distribution has no modes or no value around which the observations are.
The value of X where this occurs is the one thats two standard deviations above its mean. You can apply these to assess only one variable at a time in univariate analysis or to compare two or.

Normal Distributions Review Article Khan Academy
No comments for "Two Statistics Is Used to Describe a Normal Distribution"
Post a Comment